News
Launch of the 9400 NVMe Series by Micron, Featuring U.3 SSDs Designed for Data Center Workloads

Today, Micron is unveiling their most recent solid-state drive (SSD) product for use in data centres. Micron’s success with their third-generation 9300 series, which was released in the second quarter of 2019, serves as the foundation for their 9400 NVMe Series. The 9300 series had implemented their 64L 3D TLC NAND and switched to using the U.2 form factor. The interface that they used was PCIe 3.0 x4. The drive’s maximum capacity of 15.36 terabytes allowed it to compete with the highest-capacity hard disc drives (HDDs) available on the market at the time (obviously with much higher performance numbers).
The data centre has been moving toward PCIe 4.0 and U.3 over the course of the past couple of years in an effort to unify support for NVMe, SAS, and SATA and to keep up with the performance requirements that have been put forward. Micron is producing the 9400 NVMe line of U.3 SSDs with a PCIe 4.0 x4 interface using their now-mature 176L 3D TLC NAND. This is being done with all of these considerations in mind. Because of the increased capacity per die, Micron is now able to deliver 2.5-inch U.3 drives with capacities of up to 30.72 TB. This virtually doubles the capacity per rack in comparison to the previous generation.
The 9400 NVMe series, like the 9300 NVMe series, is geared for data-intensive tasks and comes in two different versions: the 9400 PRO and the 9400 MAX. Both of these models are available for purchase. While the Micron 9400 PRO is designed to handle read-heavy workloads (1 DWPD), the Micron 9400 MAX is more suited to more general-purpose applications (3 DWPD). Both the minimum and the maximum capacity values are set at 25.60 TB and 30.72 TB accordingly. The following table provides a summary of the characteristics shared by both of the drive families.
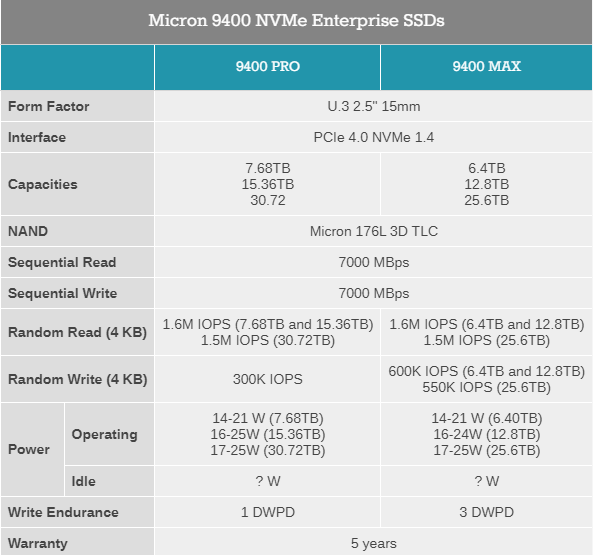
The 9400 NVMe SSD family is already in serial production for artificial intelligence and machine learning workloads, along with other HPC applications. A 77% boost in random IOPS per watt is possible thanks to the transition to a faster interface, as well as higher-performance NAND. This improvement is compared to the previous generation. In addition, Micron asserts that its enterprise SSDs offer superior overall performance across a wide range of workloads in comparison to those offered by Micron’s competitors.
The Solidigm D7-5520, the Samsung PM1733, and the Kioxia CM6-R are some of the competitors for the Micron 9400 PRO. The Solidigm D7-5520 is hampered by lesser capacity points (due to its use of 144L TLC), which results in worse performance in comparison to the 9400 PRO in all categories with the exception of sequential reads counts. The maximum capacity of the Samsung PM1733 is also 15.36TB, and its performance numbers are comparable to those of the Solidigm model. The only other U.3 solid-state drive (SSD) that can store up to 30.72 terabytes of data is the Kioxia CM6-R. On the other hand, its performance numbers in all areas are significantly lower than those of the 9400 PRO.


















