Health
The Patient’s Guide to Chronic Pain Management
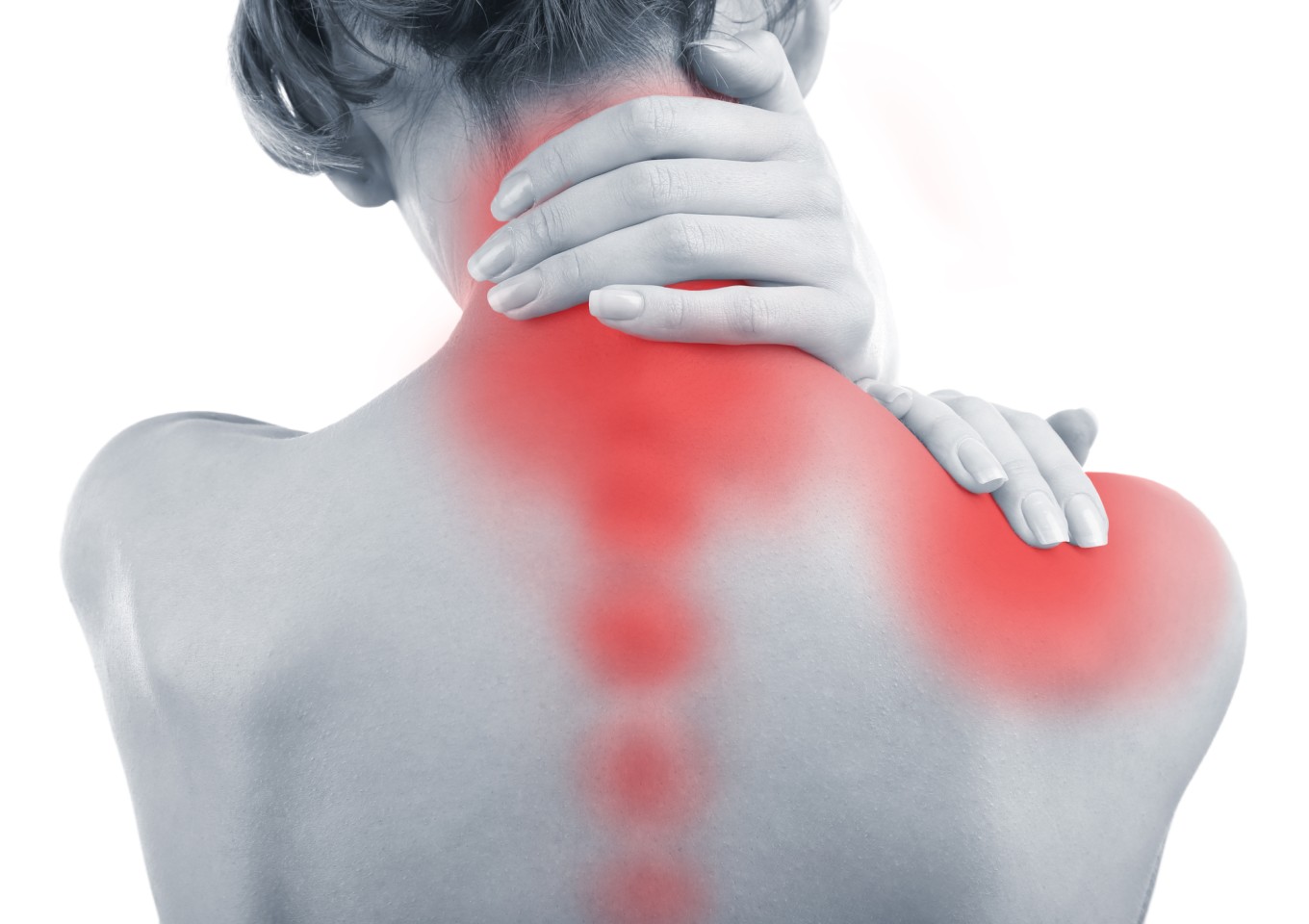
Chronic pain is a problem that 100 million people struggle with daily. It is either acute (a regular, short-term reaction to injury, trauma, or surgical procedure) or chronic (defined as chronic pain) that continues beyond normal healing times, usually three months. Chronic pain can be an extremely complex issue with complex treatment options. The patient’s guide to chronic pain management will be discussed in detail. We have to just start from introduction:
What is chronic pain?
Most pain goes away. After surgery, you recover. Your toothache is taken care of. The ankle strain gets better. A few headaches can be treated with aspirin. These are instances of temporary, or acute pain. Chronic pain is a condition that doesn’t disappear that lasts up to three months or more. Examples include knee arthritis, neck, back, or shoulders which hurts all the time, and frequent headaches from migraines. surgical pain that’s not addressed appropriately and continues to linger; injury-related muscle pain which doesn’t heal properly.
Although doctors have attempted to treat pain-stricken patients throughout time in the past, more recently, specialized education and certification in pain medicine have led to the creation of a new field of medicine that is designed to assist those suffering from chronic pain. Some professionals suggest using Integrative Therapeutics because they provide nutritional supplements to assist individuals cultivate healthier lifestyles.
There are guidelines that can be followed for the treatment of chronic pain that is caused by certain disorders, such as osteoarthritis and cancer or fibromyalgia. pain, there is often no reason for discomfort that is persistent regardless of treatment. You should know about some pain relief products we rated one of the best Relief Factor reviews.
Here are some alternatives to treatments listed in the guide, and their effect on chronic pain
-
Medications
Treatment with medication has been a successful method for those suffering from chronic pain to relieve their pain. The right treatment, with the help of opioids, may allow some to get up and perform daily tasks as well as connect with others. be productive at work and at home and experience an increase in quality of life.
-
Exercise
Patients suffering from chronic pain gain greatly by remaining as active and physically fit as they can. The basis of active therapy lies in the belief that physical therapy and/or exercise aid in restoring flexibility as well as endurance, strength as well as function and flexibility and reduce pain. The guide to the Resource Guide gives specific information on what types of exercise can benefit someone suffering from chronic pain.
-
CBT Therapy
Cognitive-behavioral therapies can help relieve pain by changing the way people think about their discomfort. CBT helps change the thinking of emotions, behaviors, and thoughts that are associated with pain, develop better strategies for coping and place the pain in a more positive perspective. Patients realize that discomfort is less disruptive to their lives and thus better functioning results.
The Resource Guide provides information about the way that medications function throughout the body, the kinds of medicines that are used to treat pain, and treatments that should be avoided, as well as highlights the importance of taking medications in a safe manner. People suffering from chronic discomfort benefit from being aware of their treatment options and, in particular, about the prescribed medication.
-
Music and Art
Music and art are both creative ways to express yourself and have been used for a period of time in psychotherapy to assist people to express their thoughts and emotions. Music and art aid in the healing process, helping to ease stress and release neurotransmitters that reduce the feeling of pain. A lot of people who engage in the arts of creation say that they feel less conscious of their discomfort.
-
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes you can manage your pain by staying as fit as you can. Should you be a smoker, seek assistance to stop smoking. Make sure you maintain the weight you are at to avoid the strain that excess weight places on knees and hips that are painful. A healthy diet is essential and exercises can alleviate or even prevent discomfort.
-
Acupuncture and the application of acupressure
Acupressure and acupuncture are both forms of traditional Chinese treatment. They ease discomfort by manipulating certain points on the body. The body is then prompted to release endorphins, which may prevent messages about pain from being sent to the brain.
What is the one thing people could be misinformed regarding managing pain?
There’s more involved in pain control than medications. A good approach to managing pain starts with a thorough diagnosis of the root cause of the problem. Then, it offers treatment suggestions aimed at specific causes to reduce symptoms and the need for medication.
Conclusion
Chronic pain can have an impact on the entirety of one’s life, not only their physical performance. The longer the present it is the greater emotional and mental anxiety a person is likely to experience. The stress can make the discomfort worse and result in a decrease in functioning. A Patient’s Guide to Pain Management provides an effective tool to those who suffer from chronic pain. It aids them in understanding the treatment options available and how to implement interventions that result in less anxiety, more positive behaviors as well as a focus on performance instead of a cure.