Guide
How to See How Much RAM Is In Your PC

Memory, also known as random-access memory (RAM), on your computer is the fast short-term memory that the computer needs for executing apps and opening files. The more RAM your computer has, the more tasks you can complete at the same time. Here’s how to find out how much software your computer has installed.
Throughout this course, we’ll also teach you how to verify the speed of your RAM memory. RAM, like virtually all technology (with the exception of batteries), is becoming better and quicker as time goes on. Those that are newer will have quicker RAM than computers that are older.
Read Also: How to Record Gameplay on PC
What Is RAM?
RAM is an abbreviation that stands for “random access memory.” This is the amount of physical working memory that your computer makes use of. All of your currently open programmes, files, and other data are saved in this location for easy access. RAM is distinct from your computer’s solid-state drive (SSD) or hard disc, which are significantly slower than RAM. When you run a programme or open a file, the data is transferred from your system’s storage to its random access memory (RAM).
The more RAM you have, the more tasks you can complete at the same time. If you don’t have enough RAM to run all of your active apps, your system will slow down because Windows (or another operating system) will have to transport data in and out of the page file on your system drive, which will cause your system to slow down. If you don’t have enough RAM, you can even get a low memory error message.
What you do will determine how much RAM you require. The newest PC games, virtual machines, and editing 4K films may all need more RAM than you may have available.
How to Check How Much RAM You Have on Windows
You can quickly determine how much RAM your Windows computer has by using a variety of methods.
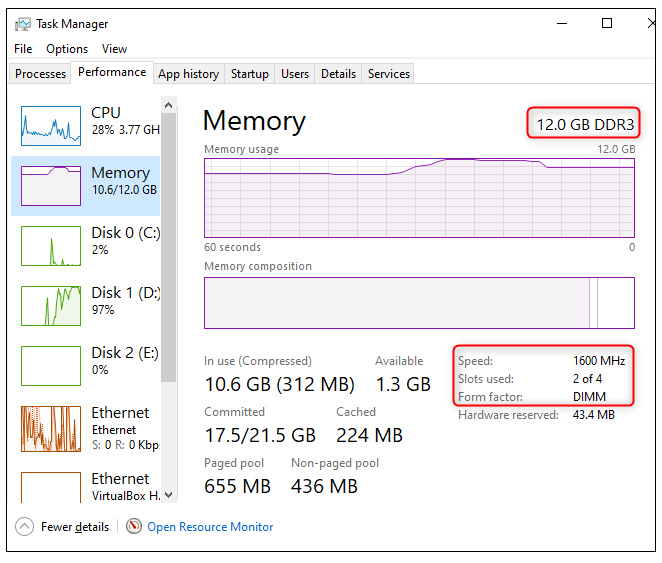
On Windows 10 and Windows 11, utilize the Task Manager to complete your task. To launch the Task Manager, right-click on the taskbar at the bottom of the screen and select “Task Manager,” or press Ctrl+Shift+Esc on your keyboard. Select the “Performance” tab and then “Memory” from the left-hand pane of the window. If you don’t see any tabs, first select “More Details” from the drop-down menu.
The entire quantity of RAM that has been installed on your computer is indicated here. The Task Manager also informs you of the standard it is using, the pace at which it operates, its form factor, and how many of your system’s physical memory slots it is now utilizing, among other things. If you are able to open your computer (which may not be possible on some laptops) and have any spare slots, you may upgrade your RAM.
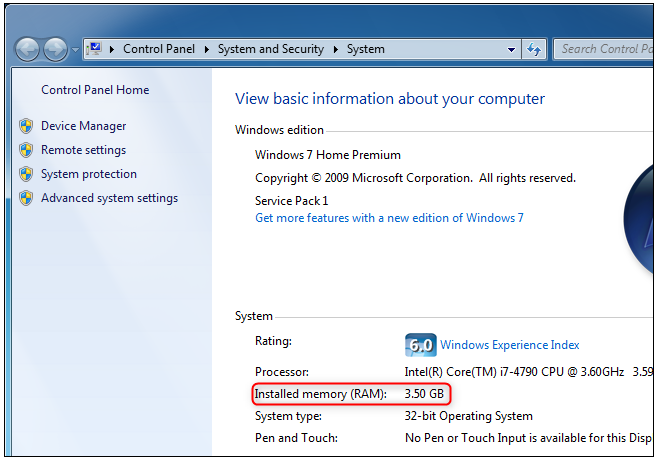
On Windows 7, the Task Manager does not provide this type of important information. The whole amount of RAM available is displayed in the Control Panel > System and Security > System page, rather than on the RAM page.
You may also get this fast by going to your Start menu, right-clicking “Computer,” and selecting “Properties” from the menu that appears. Look to the right of “Installed Memory” under System for the option “Extended Memory.”
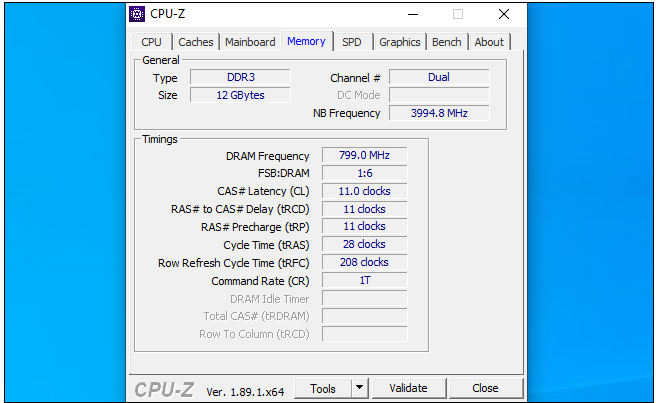
CPU-Z is a free programme that allows you to examine more detailed information about your RAM timings on any version of Windows. To see this information, download and install CPU-Z, start it, and select the “Memory” tab from the left-hand menu.
If you construct your own computer, it is possible that your RAM will not operate at the claimed timing unless you adjust the timings.
The UEFI firmware, often known as the BIOS, of your machine will typically display this information as well. This is especially useful if you’re utilizing a computer that doesn’t have a functioning operating system. Simply start it up, access the BIOS or UEFI firmware (which varies from PC to PC) using the keyboard shortcut, and check for information regarding the system’s memory or RAM.
Video




















